The Critical Role of DSPM in Enhancing Privacy and Regulation
Discover how DSPM centralizes data privacy and security by continuously assessing data posture, enabling proactive risk management and ensuring regulatory compliance.
DSPM Role in Privacy and Regulations
Integrating DSPM into privacy frameworks ensures robust data protection and adherence to regulations, safeguarding sensitive information across diverse environments.
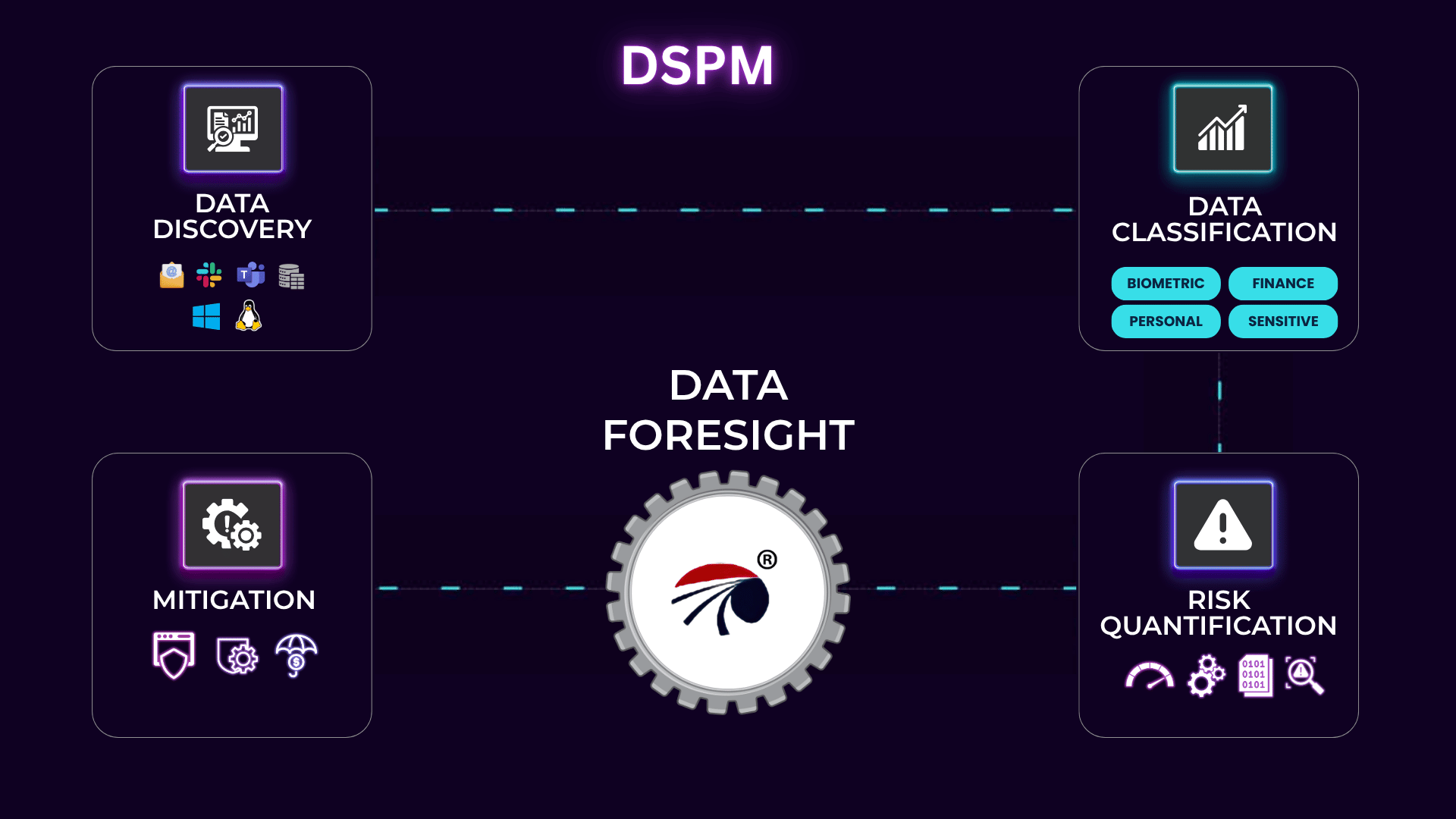
DSPM
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) unifies discovery, classification, risk evaluation, and remediation of data assets for comprehensive security oversight.
Key Benefits of DSPM for Regulation and Privacy

Data Discovery
Our Data Discovery module automatically scans your cloud and on-premises repositories to locate sensitive data, creating an accurate inventory for security operations.

Data Classification
With Data Classification, DSPM categorizes information based on sensitivity levels and business context, enabling tailored security and privacy controls.

Risk Quantification
Risk Quantification evaluates the potential impact of data exposure by correlating vulnerabilities, threat intelligence, and data sensitivity scores.

Mitigation
Mitigation capabilities prioritize and automate response workflows to address identified risks, reduce attack surfaces, and enforce remediation policies quickly.
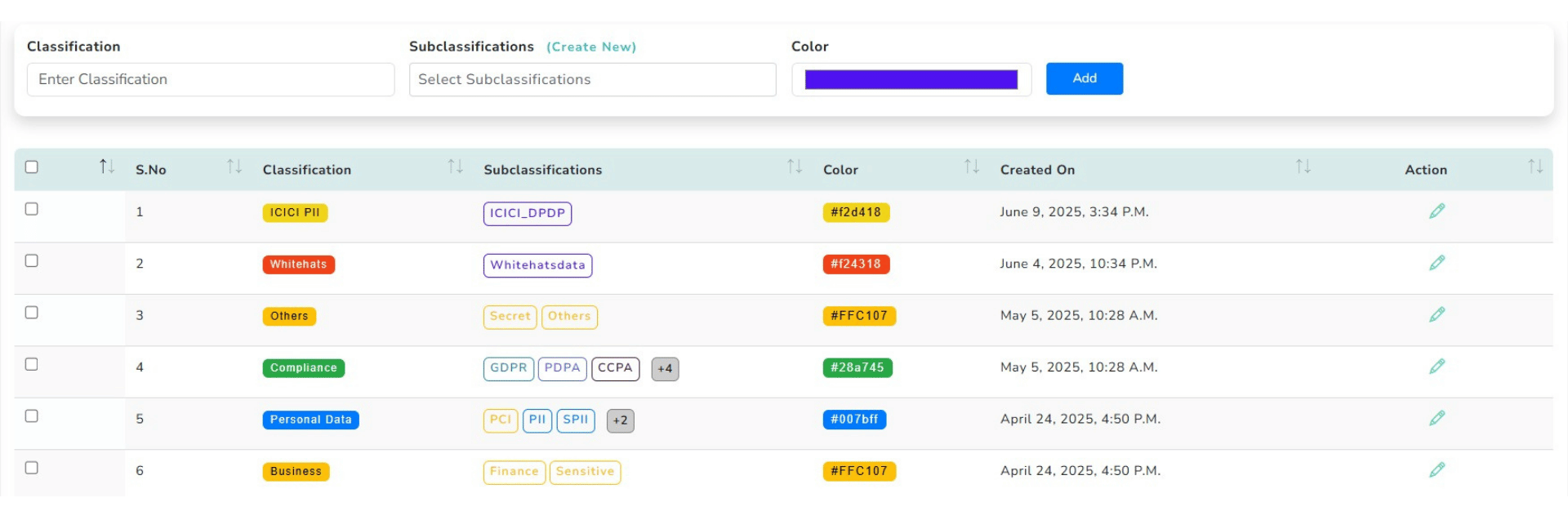
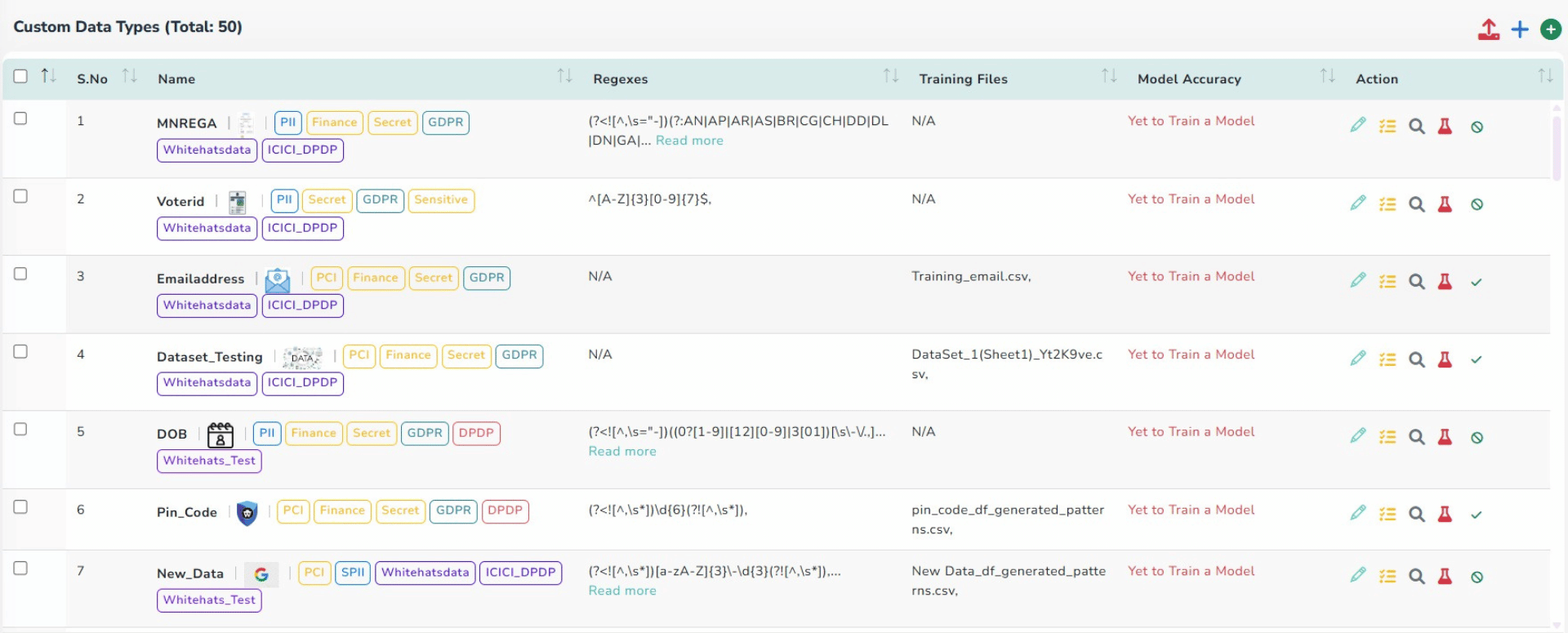
Data Type Classification Dashboards
Global Regulatory Insights in One Place
Access a unified repository of global privacy regulations, delivering real-time updates and actionable intelligence across multiple jurisdictions.

GDPR (European Union)
The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in 2016 and fully effective since 2018, sets strict rules for collecting, processing, and storing personal data. It covers identifiers such as names, addresses, emails, and online identifiers, and grants rights including access, rectification, and erasure.

CPRA (California)
California’s Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) strengthens resident privacy by expanding CCPA rights and increasing transparency over data collection and use.

DPDP Act (INDIA)
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP) safeguards individual privacy by regulating the collection, storage, and processing of personal data, setting clear usage guidelines and promoting compliance with modern privacy standards.

PIPEDA (Canada)
Enacted in 2000, Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) regulates personal information in commercial activities, protecting privacy while supporting organizations’ legitimate data use.

LGPD (Brazil)
Brazil’s Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), in force since August 2020, regulates the collection, use, and processing of personal data to safeguard privacy and align Brazil with international data protection standards.

PDPA (Singapore)
Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA), enforced by the Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC), establishes a framework for responsible personal data use that balances organizational needs with individual privacy and strengthens trust in the digital economy.

PDPA (Sri Lanka)
Sri Lanka’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) safeguards individuals’ privacy by regulating how personal information is handled, setting data-security standards, and requiring responsible processing aligned with global practices.

PIPL (China)
China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) strengthens privacy protections by imposing comprehensive requirements for data handling, consent, and cross-border transfers, aligning with global data-protection standards and ensuring regulatory compliance.
DPL (Chile)
Chile’s Data Protection Law (DPL) sets strict requirements for handling personal data, safeguarding privacy and requiring compliance with global standards and robust security practices.

PDPL (Saudi Arabia)
Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL) safeguards personal data with clear processing rules, enhancing transparency and accountability while aligning with global standards.

PIPA (South Korea)
South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) safeguards personal data with strict standards for collection, use, and security, strengthening privacy rights and regulatory compliance.

CDPA (Virginia)
Virginia’s Consumer Data Protection Act (CDPA) gives residents greater control over their personal data and imposes strict requirements on businesses for data collection, use, and storage to enhance privacy and security.

TDDDG (German)
Germany’s Telemedia Data Protection Directive for Digital Goods (TDDDG) mandates strict data-handling and security standards for digital transactions and media services, strengthening consumer trust and regulatory compliance.

CTDPA (Connecticut)
Connecticut’s Data Privacy Act (CTDPA) protects residents’ personal information by imposing strict rules on data collection, use, and sharing, emphasizing transparency and security to empower consumers.

UCPA (Utah)
Utah’s Consumer Privacy Act (UCPA) protects residents’ personal data by regulating how businesses collect, use, and share it, setting clear rules for transparency, control, and security.
CPA (Colorado)
Colorado’s Privacy Act (CPA) protects residents’ privacy by setting clear rules for how businesses handle personal data and giving consumers control over its collection, use, and sharing.

nFADP (Switzerland)
Switzerland’s new Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP), effective September 1, 2023, modernizes privacy law to align with the GDPR, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and stronger individual rights.

PDPA (Thailand)
Thailand’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) establishes a robust, internationally aligned framework for privacy, enforcing strict rules on the collection, processing, and storage of personal data.